I’ve received so many questions about the differences between cellars and basements recently that I’ve decided to dedicate a whole article to this topic.
While a cellar might be very similar to a basement on the surface, there are some important differences.
To be honest, the definition of these terms is not uniform throughout the country and many people use them interchangeably. That often can be really confusing, and that’s something you have to keep in mind.
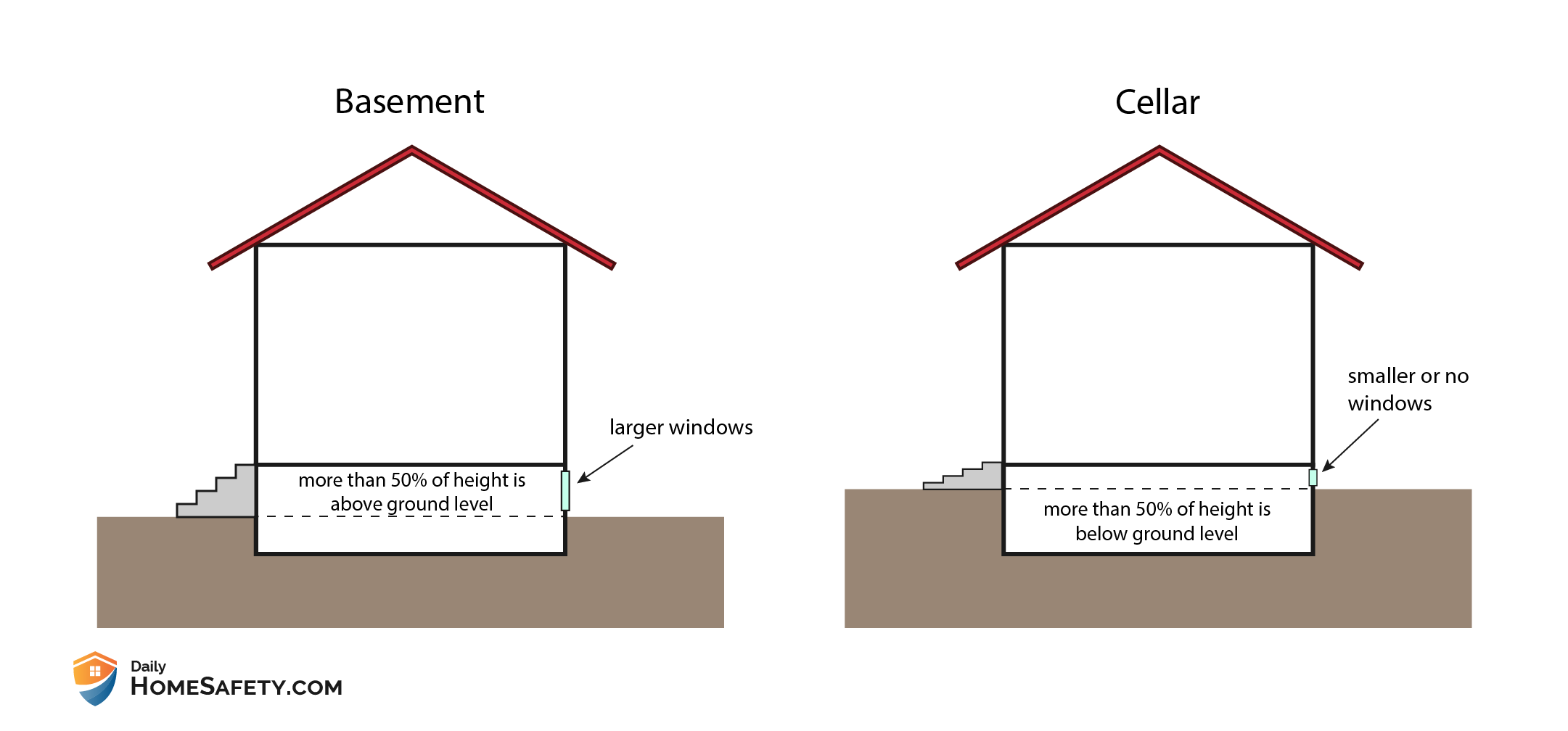
In most cases, the basic difference between a basement and a cellar is that a basement is not fully below curb level. A cellar is usually located deeper below the ground level than a basement but that’s not a rule set in stone. However, there are other characteristics that help to distinguish these spaces.
My goal is to show you how to recognize all the main differences between a basement and a cellar quickly and easily so that you know what you’re dealing with.
At the end of the article, I also included a useful table where you can find the most important differences all in one place.
What Is a Cellar? How Is It Different From a Basement?
By definition, a cellar is a room (or rooms) partially or completely below ground level beneath a building (typically a house).
A cellar is mainly used for storage purposes (food and other stuff) and in most parts of the country, it’s not considered a floor (unlike a basement).
A cellar is either completely or partially underground but in the latter case, more than half of its height has to be below ground level otherwise in most areas it’s considered a basement.
If you need to be sure that you’re dealing with a cellar, I suggest you also check the local housing codes. For instance, in New York City the main difference between a cellar and a basement is the amount of height above curb level: a cellar has less than half of its height above curb level.
There are many situations when it’s important to be aware of the local laws and rules. For example, in NYC a cellar in one- and two-family homes can’t be lawfully rented and can’t be used as a living space.
Another characteristic of a cellar is that it usually has only small windows or no windows at all. Small in this case means that a person can’t fit through it. Thus, even if it has windows, they can’t be used as an emergency exit.
As a consequence, a cellar usually receives no direct sunlight and less natural light than a basement. Of course, most cellars are equipped with electricity, therefore they’re not necessarily dark places.
A cellar can be a perfect storage space, especially if it has concrete walls and flooring with low to moderate indoor humidity.
The entrance of a cellar is often located outside the building, however, that’s not a rule. Sometimes you can get into a cellar without having to leave the house.
Several types of cellars exist.
A root cellar is used for storing vegetables, fruits, and other kinds of food. A root cellar can be especially useful if you grow your own vegetables and want to have a larger supply at hand. It works best in colder climates as the temperature shouldn’t go above 40ºF in order to keep the vegetables fresh.

Another common type is called wine cellar. It’s an underground room designed especially for storing wine and other alcoholic beverages. Wine requires a special storage environment (constant temperature and negligible light exposure) and a well-planned wine cellar is a perfect place to keep your bottles.
What Is a Basement?
A basement is a floor of a house that’s usually located partly below ground level. In most cases, it has more than 50% of its height above curb (or ground) level. Basements that are not fully below the ground are sometimes also called semi-basements.
A basement can have an exterior entrance (walk-out basement) but it almost always has an interior one so you don’t have to go outside to get access. A basement with larger windows and usually no exit to the outside is called a daylight basement.
It usually has relatively large windows that make it brighter than a cellar. In most cases, they can also be used as emergency egress windows. Regarding safety, it’s a pretty important difference between a basement and a cellar.

As I’ve already mentioned, a basement is considered a floor and it can be used as a habitable space. In many areas, a basement floor can be rented and used as an apartment.
However, not all basements are the same.
While an unfinished basement is often used as a storage room (like a cellar), a finished basement is suitable for many purposes, such as a bar, game room, home gym, kitchen, or media room. Often it can be used as a living space or a spare room as well.
A finished basement can be very similar to other rooms of the house, with the same (or similar) type of flooring, lighting, ventilation, and heating.
As basements (like cellars) are under the ground level, they can be pretty easily flooded. To prevent this situation and avoid water damage, homeowners usually install a sump pump in the basement that removes excess water and protects the room (and the house).
As a side note, a sump pump is also often present in a crawl space. By the way, you can find a handy list of the most common causes of sump pump failure here (some useful preventive measures included).
Other common appliances that you’ll often find in a basement are a water heater, dryer, washer, and dehumidifier to eliminate excess moisture.
The major advantage of a finished basement is that it adds extra living space to your home. Any basement provides an additional room that you can use according to your needs. For instance, you can store stuff there that you want to be easily accessible but not in plain sight.
Main Differences Between a Cellar and a Basement
Although the definitions vary across the country, there are some key differences between basements and cellars that in most cases help you distinguish one from the other.
First of all, a cellar usually has more than half of its height under the ground while the floor of a basement is more close to the level of the ground.
Regarding size, cellars are usually smaller than basements and they’re used for a specific purpose, such as storing food. By contrast, a basement can be used for many different purposes.
In the vast majority of cases, a cellar cannot be used as a bedroom or any other living space and cannot be rented either.
Concerning accessibility, a basement usually can be reached from the inside while a cellar often only has an exterior entrance, so you have to leave the house if you want to enter it.
While both spaces can have a dirt floor for storing “dirty stuff” (coal, for instance), this is more typical of a cellar.
Another difference is that a finished basement can be included in the square footage in certain situations while a cellar doesn’t really count as square footage. However, more often than not you won’t get the same price per square foot as for the other parts of the house.
While you can’t really add a basement to an existing house (at least it’s not something most people would consider), a cellar can easily be built in your yard separately from the house. This can be a major advantage if all you need is a place to store food or wine.
Cellar vs. Basement: Comparison Table
| Cellar | Basement | |
| Definition | 50% of its floor-to-ceiling height is below the curb | 50% of its floor-to-ceiling height is above the curb |
| Size | usually smaller | can be as large as the floor area of the building |
| Uses | storage (mainly food or wine) | storage, workout room, guest room, kitchen, laundry room, office, game room, etc. |
| Entrance | access from the outside and sometimes from the inside | access from the inside and sometimes from the outside |
| Windows | tiny windows or no windows | larger, often full-size windows |
| Emergency exit | no | windows have an emergency egress function |
| Living space | no | a finished basement often can be used as a habitable space |
| Renting | cannot be rented | can be rented if it meets the requirements |
| Presence of rodents | more common | less common |
| Dirt floor | common | less common |
| Cost of heating | heating is usually not necessary | heating cost can be significant when used as a living space |
| Separate from house | possible | not possible |
| Shelter function | a cellar is located deeper in the ground, thus it provides better protection against certain types of extreme climate events | less protection against extreme weather |
Summary
As you can see a cellar and a basement are not the same things, although in some regions of the US people use the terms interchangeably.
By now, you’re aware of all the main differences between a basement and a cellar. In my experience, most people would benefit more from a basement as it can be used for more purposes.
Also, a basement not only increases the value of a property more than a simple cellar but also provides more extra space. Of course, the cost of maintaining a basement is usually higher than that of a cellar, especially if you use it as a living space.
On the other hand, finishing a basement can be pretty costly compared to a cellar. If all you need is a simple storage space for food or other things that can’t be ruined by high humidity, a cellar might be the better choice.
Photos: Wikimedia (Chris Light)